- Designed to help address the challenge of soft tissue failures

ELEOS™ LIMB SALVAGE SYSTEM
Helping to address soft tissue failures and aseptic loosening, all in a personalized, simplified fashion
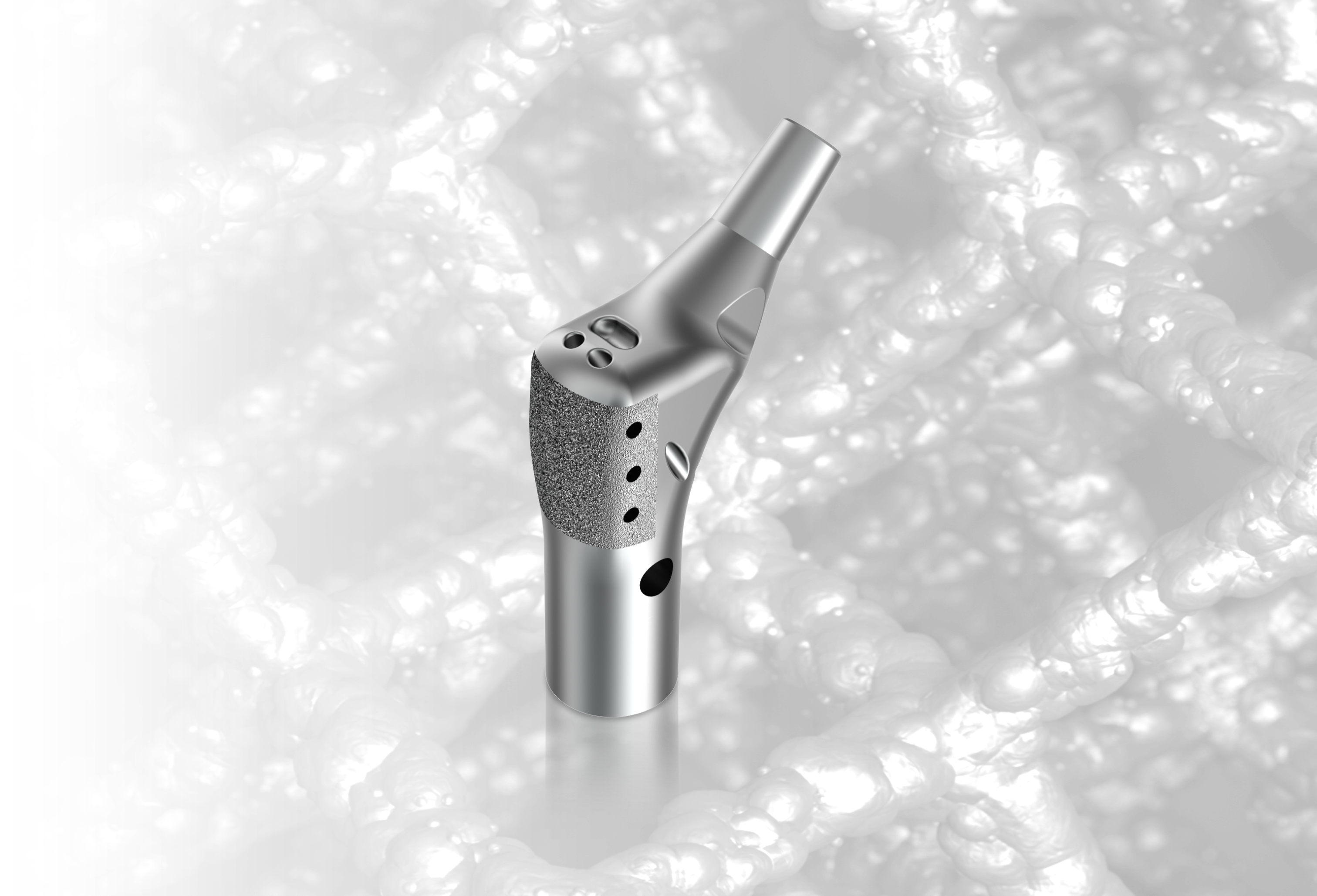

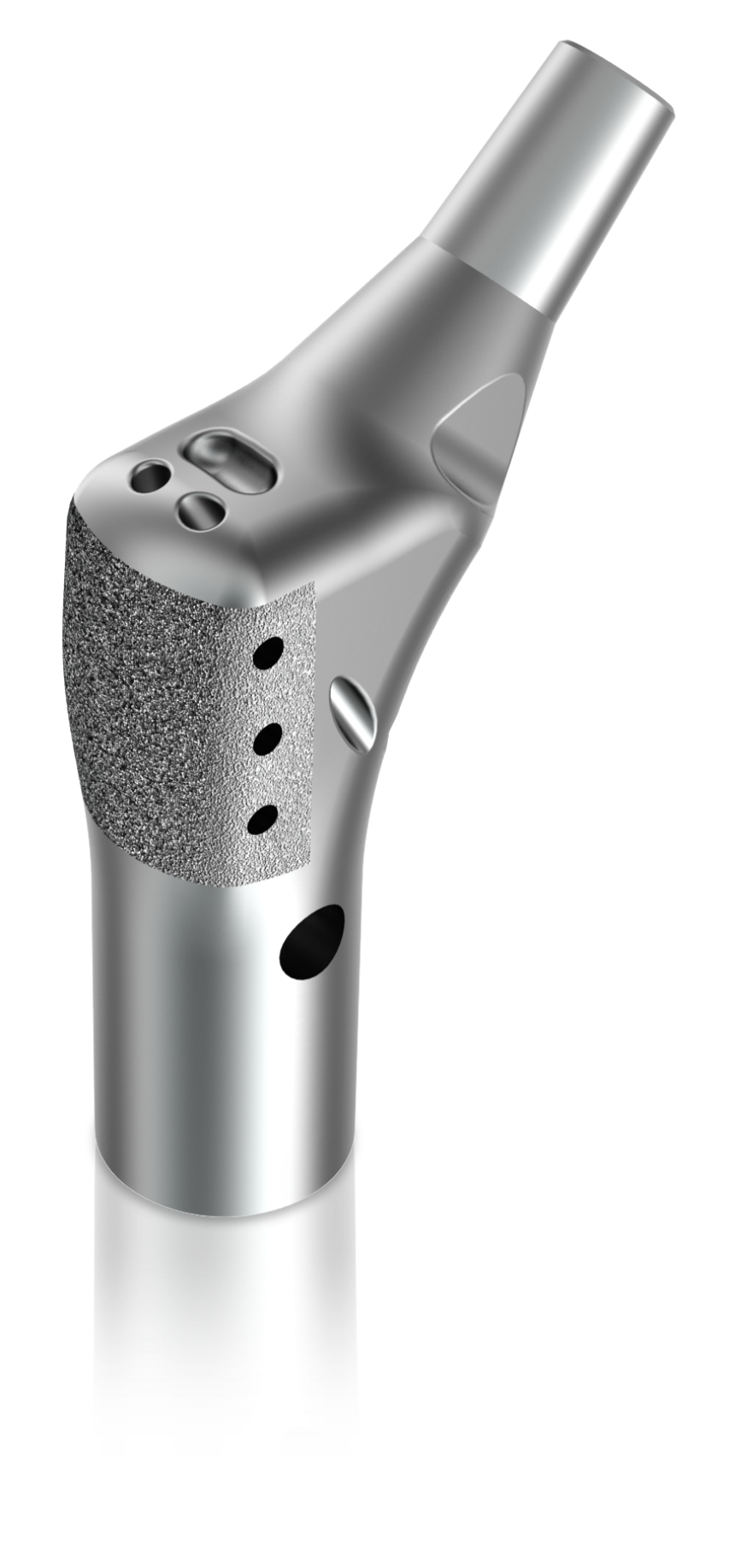
ELEOS™ Proximal and Total Femoral Replacement

Addressing the challenge of soft tissue failures:
19% of oncologic proximal femoral replacements fail due to soft tissue attachment failures1
Addressing the challenge of soft tissue failures:
19% of oncologic proximal femoral replacements fail due to soft tissue attachment failures1

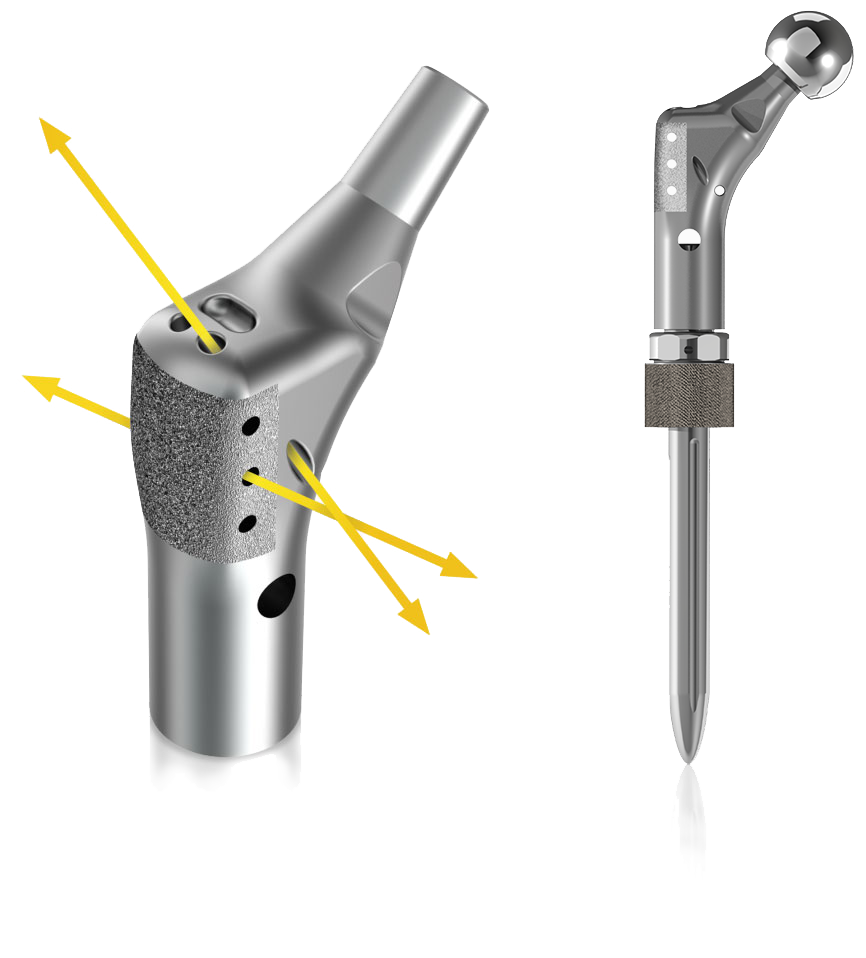
Anatomic design with suture holes to allow for the fixation of adjacent soft tissues
-
 Anatomically aligned suture holes
Anatomically aligned suture holes - Provide directional anatomic fixation of adjacent soft tissues
- Holes are oriented Superior lateral to Inferior medial, anterior to posterior
-
 Plasma sprayed surface
Plasma sprayed surface Located laterally to support soft tissue apposition
-
 Anatomic design with 15° of built in anteversion and 135° neck angle
Anatomic design with 15° of built in anteversion and 135° neck angle - Design mimics natural anatomic structures
- Supports improved alignment of bowed canal-filling stems and total femoral replacement
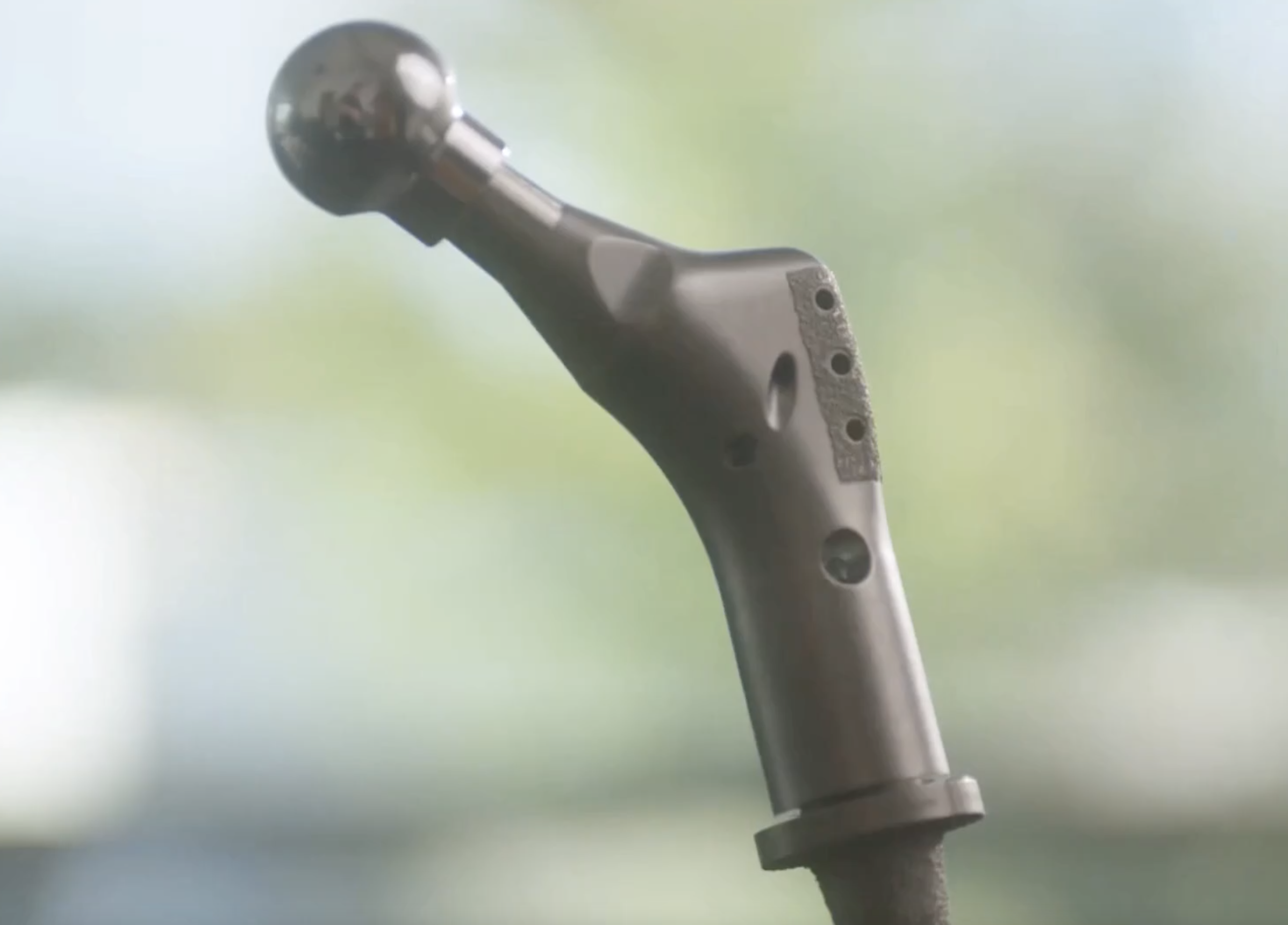

Product information
Limb Salvage System
ELEOS™ and ELEOS™ with NanoCept™ Technology Limb Salvage System
Schedule a demonstration with us now.
References
1. Henderson, et al. Failure Mode Classification for Tumor Endoprostheses: Retrospective Review of Five Institutions. JBJS, 2011 Vol 93-A, No 5, 418:429