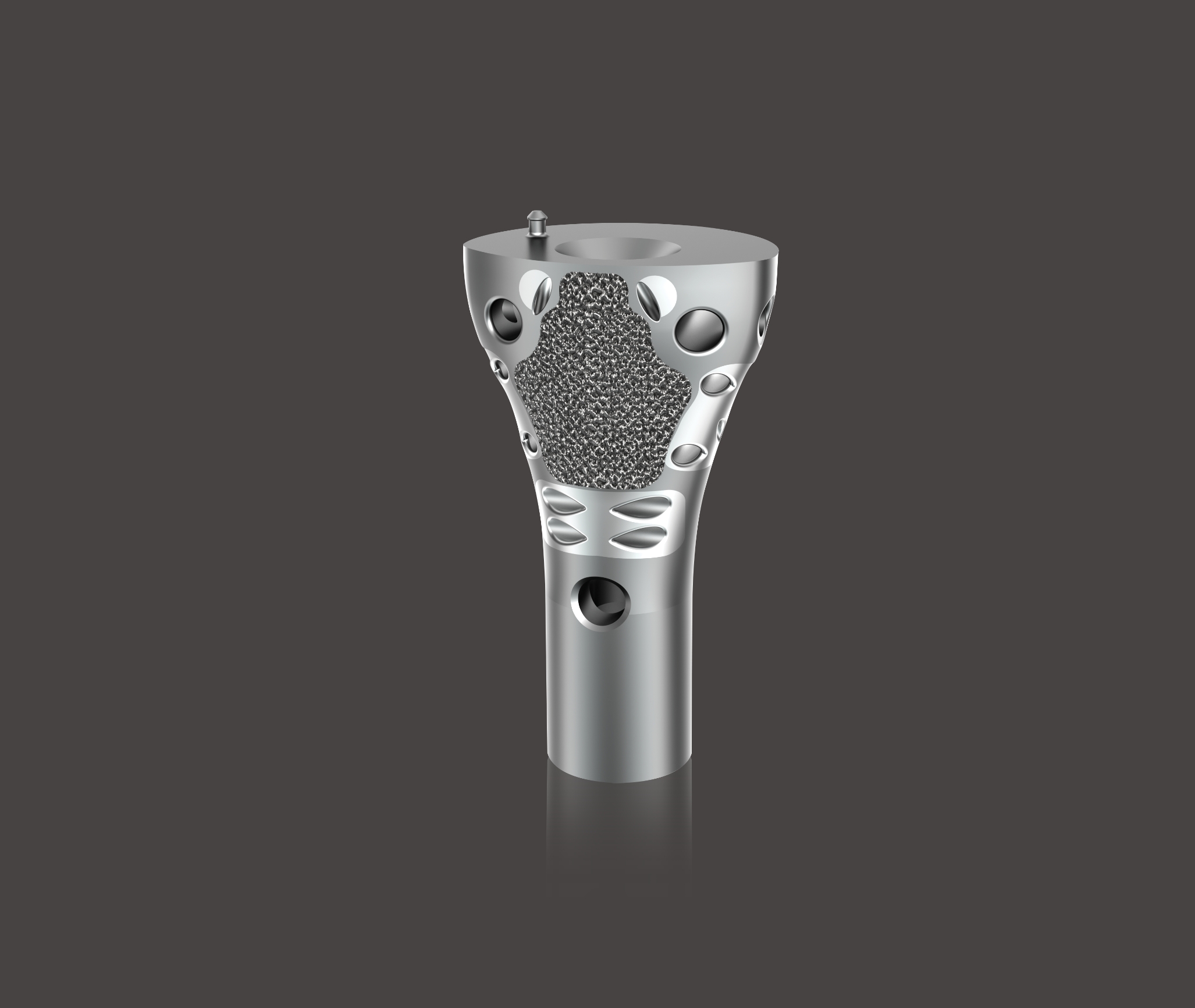
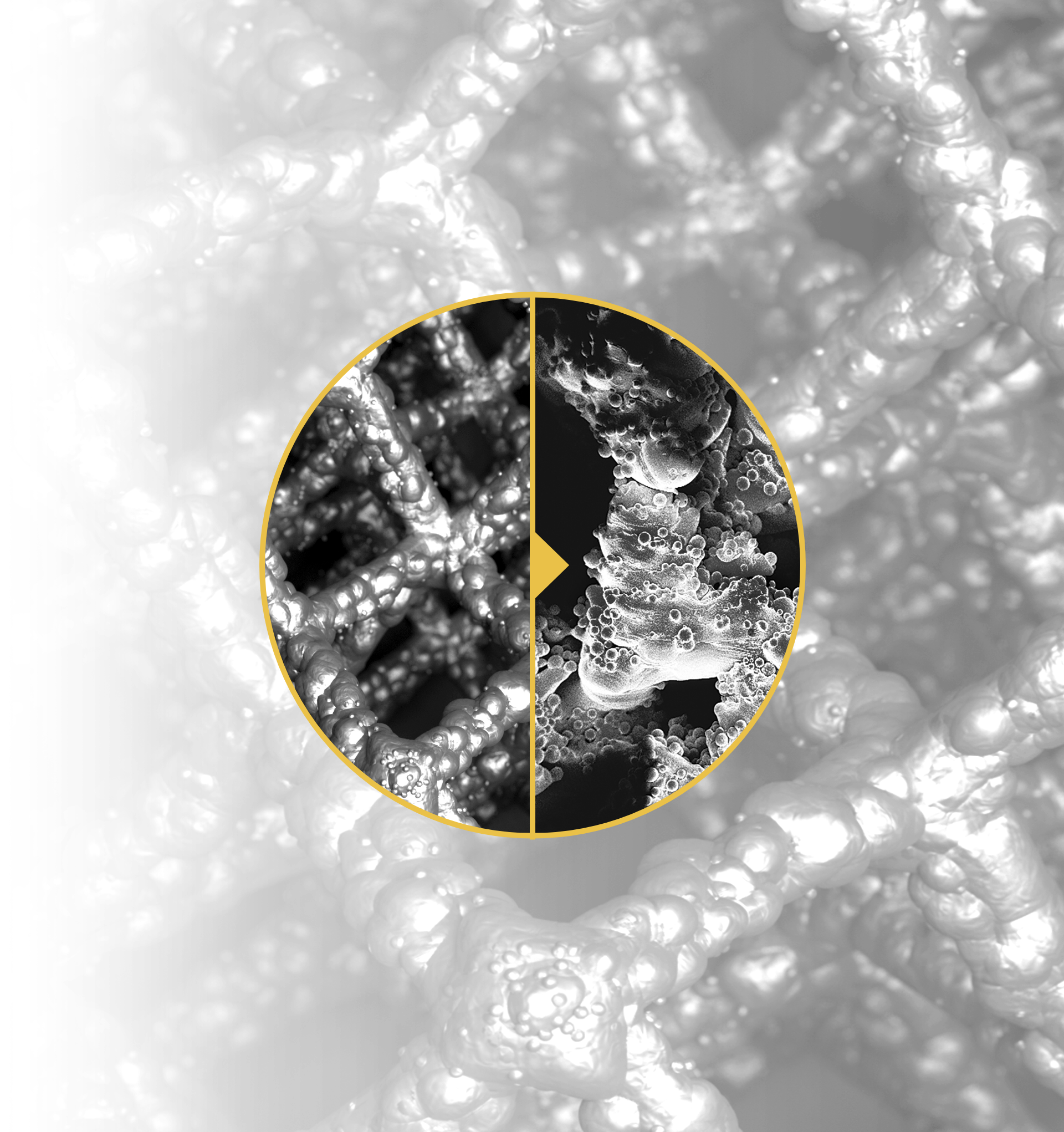
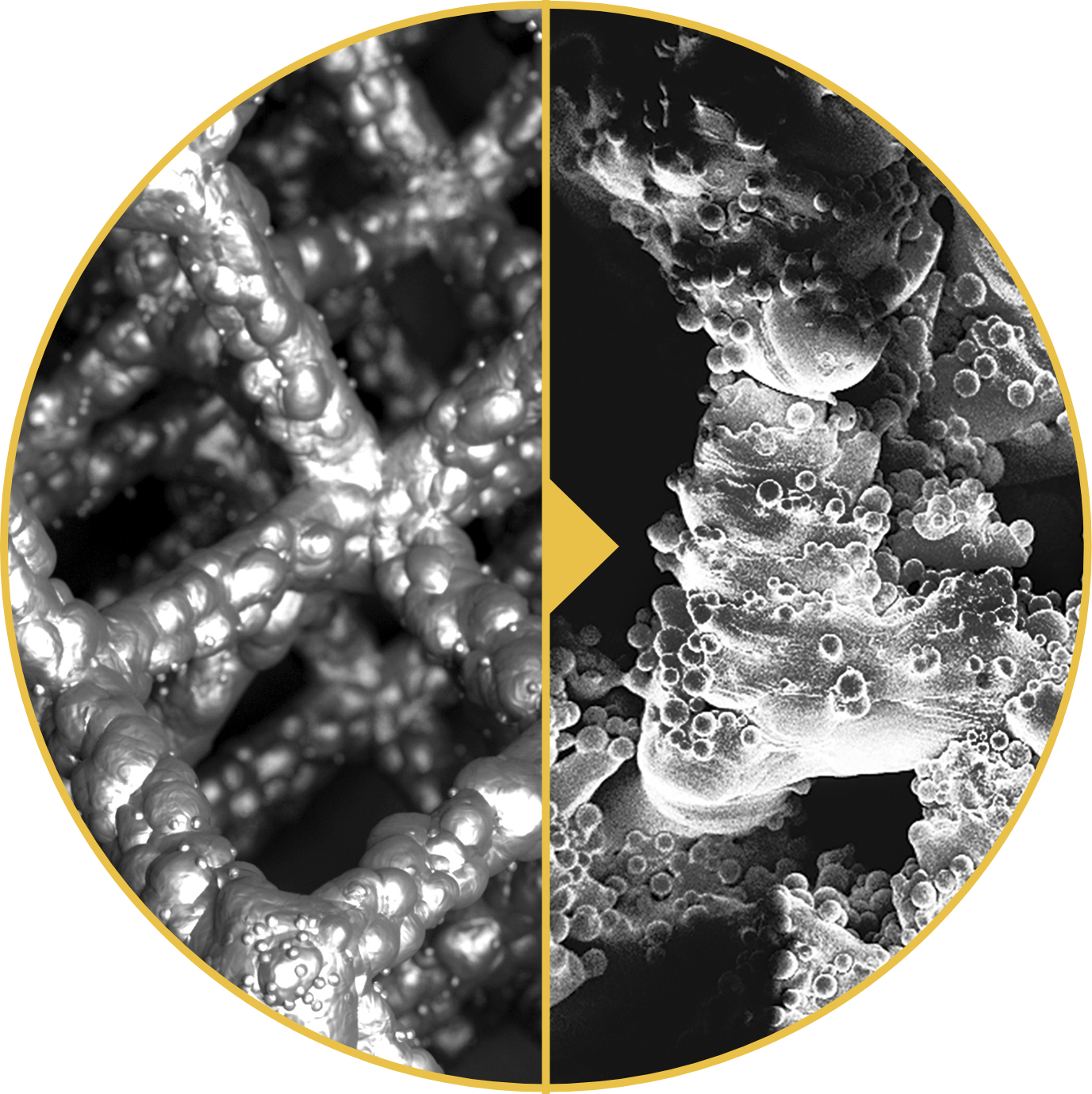
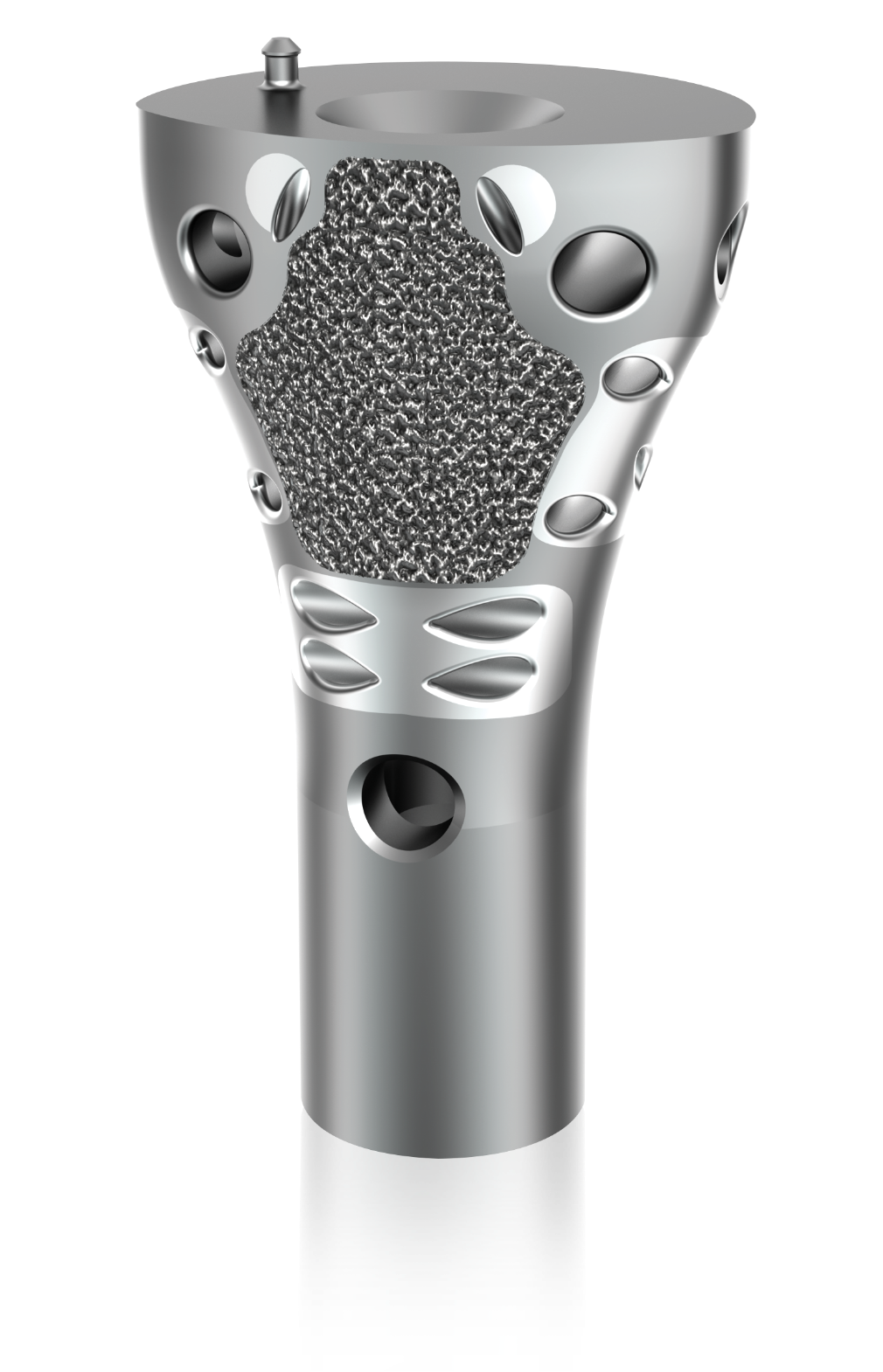
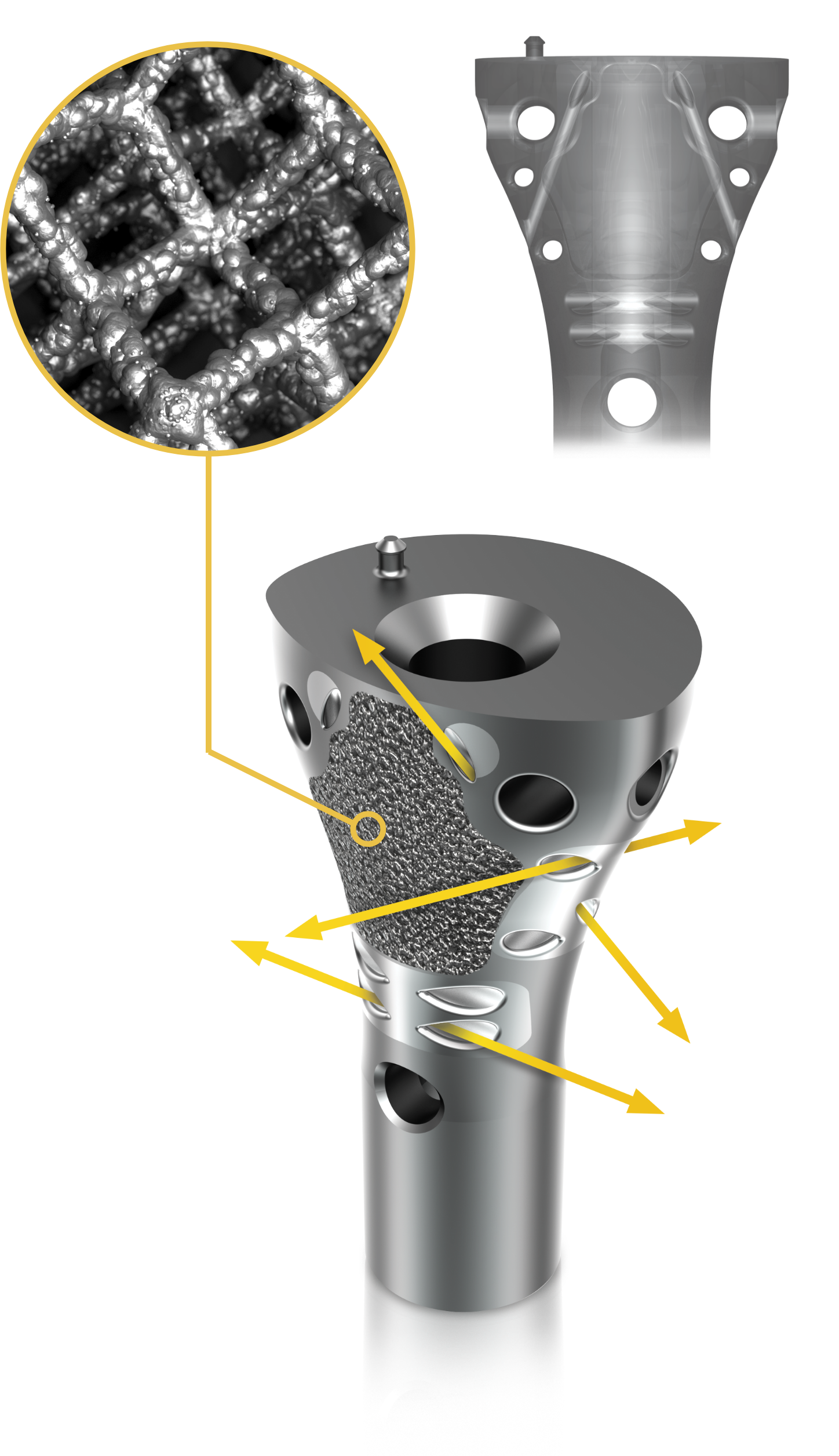
1. Henderson et al. Failure Mode Classification for Tumor Endoprosthesis: Retrospective Review of Five Institutions and a Literature Review. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2011;93:418-429. doi:10.2106/JBJS.J.00834. 2. Mumith, et al. Augmenting the osseointegration of endoprosthesis using laser-sintered porous collars. The Bone and Joint Journal. Vol. 99-B, No. 2, February 2017. 3. Cauthup, et al. Long-Term Survival of Cemented Distal Femoral Endoprostheses with a Hydroxyapatite-Coated Collar. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:1569-75. 4. Promimic. Increased Fixation and Integration of Titanium – In vivo studies in a rabbit tibia model. Data on File. https://www.promimic.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Increased-Fixation-and-Integration.pdf. 5. Promimic. Introducing Hydrophilicity to your implant. Data on File. https://www.promimic.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Introducing-Hydrophilicity-to-Your-Implant-spread.pdf. 6. Data on File, Onkos, 2020. 7. Taniguchi, et al. Effect of pore size on bone in-growth into porous titanium implants fabricated by additive manufacturing: An in vivo experiment. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. Vol. 59:690-701. February 2016. 8. Dickey, et al. Pore Size and Morphology Modulate Strength of Soft Tissue In-Growth into Porous Titanium Implants. Poster No. 1865 • 54th Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 9. Dickey, et al. Pore Size Modulates Strength of Soft-Tissue In-Growth and Growth Factor Expression in Novel Porous Titanium Implants. Poster No.2213 • 55th Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society.